Ulcerative colitis, or UC as it is commonly known, is a chronic, lifelong condition which is part of a group of conditions known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Ulcerative colitis, or UC as it is commonly known, is a chronic, lifelong condition which is part of a group of conditions known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It causes inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract (gut). This inflammation occurs in the colon (large intestine) and rectum. Small ulcers can develop on the colon’s lining which produce pus and mucus. This can cause abdominal discomfort and frequent emptying of the colon.
The other main type of IBD is Crohn’s disease. UC and Crohn’s disease share some of the same symptoms, but it is important to understand that they affect different areas of the gut.
While Crohn’s disease can affect any of the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) UC just affects the colon (large intestine) and rectum. Crohn’s disease can also affect the entire thickness of the digestive tract wall, while UC only involves the innermost lining of the colon. Crohn’s disease may also skip areas - meaning you could have inflammation near you mouth and also in your small bowel but no where in between.
UC is thought to be an autoimmune condition.
There is no known cure for UC. Some people have surgery to remove parts of their colon and rectum which are affected but inflammation could return at another time if any of the colon, rectum or anus is left and even then surgery doesn’t necessarily remove all of the symptoms and complications of IBD.
It is thought that around 1 in 7 people with the disease have a close relative who is also a sufferer.
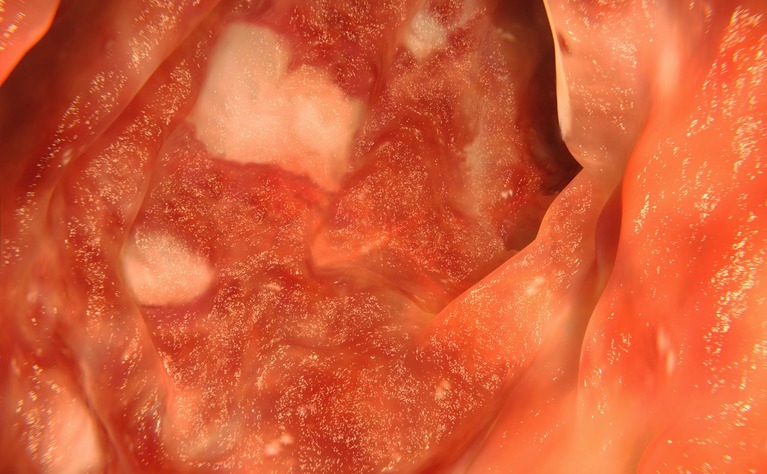
Common ulcerative colitis symptoms include:
Some of the other UC (ulcerative colitis) symptoms include:
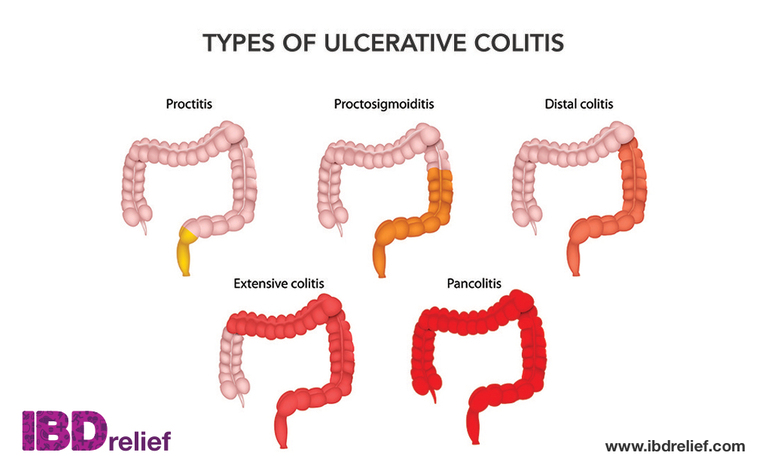
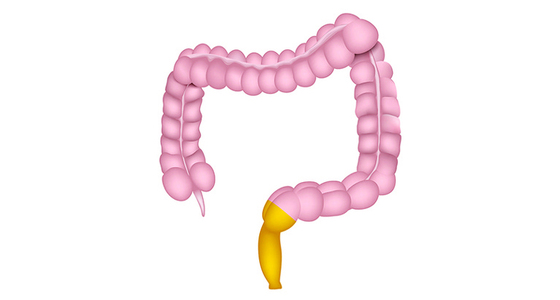
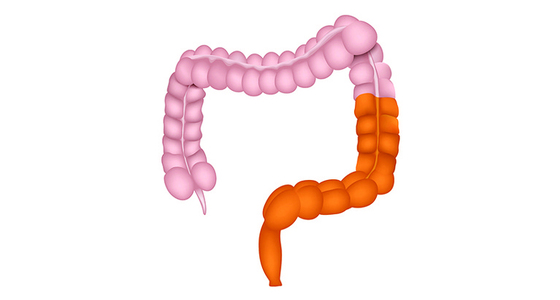
Depending on where you have inflammation will depend on the type of UC you have. The types are:

There is no one method of diagnosing UC. If you have been suffering from UC-type symptoms for several weeks or more then the following tests may be carried out:


Unfortunately there is no known cure for UC. The main methods of treating ulcerative colitis used by healthcare are:

Some people also make changes in their lifestyle to help manage some of the life-affecting symptoms of the condition.
These include:
No one really knows what the exact cause of UC is. The cause is often put down to a number of factors including:
Scientists continue to carry out research into the causes.
There are millions of people around the world who suffer from UC so it’s important to remember that you are not alone. It can affect people of all ages, however it most commonly first develops between the ages of 15 - 25.
People with UC often go through periods of flare-ups where they have severe symptoms and periods where their symptoms are more mild or non-existent. Someone with the disease who isn’t displaying any symptoms is known to be in remission.
Over time there are various complications that can occur as a result of UC. These include: